What’s The Difference Between Polyester and Polyether?
There are two primary types of polyurethane – polyester, and polyether. Both are useful in a multitude of industrial applications. Both are urethane elastomers. So what’s the difference?
Polyurethane Typical Elastomer Characteristics
The term elastomer — a contraction of the words elastic and polymer. Elastomers cover a group of linear polymers that exhibit a large range of elastic deformation under load. Often, they can be stretched to several times their original size. Release the force and the part will return to its original shape. This is repeatable with similar results. Polyurethane’s elastic properties are the result of a change in the distance between adjacent atoms — bond length — when under load. Hooke’s law will generally apply such that twice the force produces twice the stretch. Remove the load and the interatomic forces return the atoms to the original position. The elastic deformation recovers in full.
Polyester
- Oil/solvent resistance
- Resistance to weak acids/basics
- Abrasion resistance
- Excellent mechanical properties
- Fungus Resistance
- Excellent Vibratory Dampening
Polyester polyurethane is not recommended for use where high humidity or water exposure is a concern. Hydrolysis is a risk which will have a negative effect on the physical properties of the polyurethane.
Polyether
- Low-temperature flexibility
- Excellent hydrolytic stability
- Food Grade Applications
- Temperature resistance
- Excellent mechanical properties
- Weather (UV) resistance
Polyether polyurethanes are recommended for applications which are expected to experience medium to high stress.
Abrasion Resistance Properties
Without question, the urethanes have outstanding abrasion resistance. They outwear metals, plastics, and other rubbers by a wide margin — often by 8 to 1 or more. Abrasion results from many actions, such as impingement, erosion, impact, scuffing, and sliding.
Sliding refers to scraping and rubbing abrasion. Impingement refers to particles or objects striking the urethane surface at a high angle.
Polyester polyurethane exhibits superior sliding abrasion resistance. This makes it it better suited for applications like scraper blades.
Heat Resistance Properties
Polyurethane elastomers can withstand continuous use up to 194°F (90°C). Flame retardants may be added to the formulation, if required. Both polyester and polyether urethanes perform well at high temperatures. But polyesters are better able to withstand high temperatures longer and are more resistant to heat aging.
Polyethers are less susceptible to dynamic heat build-up.
Low-temperature flexibility
Polyurethane elastomers get harder as temperatures drop. This makes them less flexible and potentially brittle. Depending on the formulation, the brittle point may be between -40°F and -100°F (-40°C and -73°C). Of the two polyurethane types, polyether polyurethane is less affected by cold temperatures.
Polyurethanes can withstand sudden and dramatic temperature drops without cracking. And even at their highest hardness levels, polyurethanes have a better impact resistance than most plastics.
Rebound properties
Some products need to return the energy they absorb (rebound). Polyether polyurethane provides higher rebound than polyester polyurethane.
Shock absorption properties
Sometimes you want the product to absorb the energy it receives (opposite of rebound). In this case, polyester urethane is the better option (e.g. vibration dampening applications).
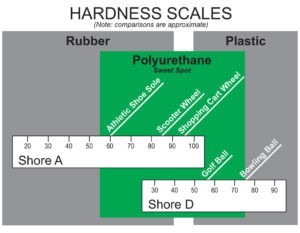
Hardness Scales. Note: the durometer “A” scale is used for the softer urethanes. The durometer “D” scale is used for the harder urethane compounds (above 95 A durometer).
Both polyester polyurethane and polyether polyurethane can be made to any hardness from soft to hard.
Cut and tear resistance
While both polyether and polyester polyurethanes are strong, polyester polyurethanes have a higher tensile strength and a higher cut and tear resistance than polyether polyurethanes.
Water and moisture resistance
Polyether polyurethanes should be selected if the product is to be placed under water or exposed to high humidity as they exhibit excellent hydrolytic stability.
Polyether polyurethanes can be stable in water as warm as 122°F (50°C) for long periods of time. However, they are not recommended for continuous use in water over 158°F (70°C). You can expect .3% to 1% increase in weight due to water absorption and there is a negligible swell in volume.
Polyester polyurethanes are not recommended for applications where water and high humidity is a concern.
Oil and chemical resistance
Polyester polyurethanes are more resistant to exposure to oils, fuels, or chemicals.

